Ramayana in Hampi
Hampi has a phenomenal number of attractions believed to be associated with Ramayana, the Hindu epic.

R
amayana , literally means the story of Rama , is one of the sacred texts of the Hindus. According to various estimates, the epic poem was first composed during 500 BCE and 100 BCE.Ramayana is told in 7 cantos (kandas) and tells to story of Rama, Sita and the demon king Ravana of Lanka who abducted Sita to Lanka. The central theme and moral of Ramayana is the victory of good over the evil.
The main character, Rama is attributed as one of the ten incarnations of Lord Vishnu. Interesting in this incarnation, Rama is portrayed with humanly values and weakness rather than the godlike supernatural powers.
As mentioned earlier Ramayana is told in seven kāndas or chapters .
The first chapter - called Bala Kānda - deals with Rama’s birth in the Ayodhya kingdom and his childhood heroics. The chapter then narrates how Rama won Sita, the princess of Mithila.
It is believed that the place mentioned in Ramayana as the birth place of Rama is the modern day Ayodhya in the Uttar Pradesh state.
The next chapter - Ayodhya Kanda - narrates the events that eventually led to the exile of Rama. Dasaratha, the king and father of Rama decides to handover the mantle to his son. Kaikeyi , the youngest of Dasaratha’s three wives wants her son to be the new king. She asks for the two boons , once Dasharatha granted her. Send Rama in exile to the forest for 14 years and her own son Bharata made the crown-prince. Rama prepares to leave for forest. Lakshmana joins him , so is Sita.
The third chapter - Aranya Kanda - narrates the trios life in the forest and the abduction of Sita by Ravana, the demon king of Lanka. Ravana sends Maricha, the demon, as a ploy in the form of a golden deer. Sita desires the deer and Rama chases it to catch alive. Quickly Rama realizes the ploy and decides to kill the demon with an arrow. The trick works. The demon cries allows “Ah Lakshmana!” in Rama’s voice.
On hearing this Sita compels Lakshmana to go and aid Rama. Once Rama and Lakshmana away from the hermitage, Ravana abducts Sita and takes her to Lanka by his flying chariot. Rama and Lakshmana starts the search of Sita.
The fourth chapter - Kishkindha Kanda - has some special significavce to the mythical landscape of Hampi. Rama and Lakshmana reaches Kishkinda, the kingdom of monkeys (Vanara Kingdom) . According to the local folklore, the events in this episode happened in the environs of Hampi. The geography of Hampi stand as proof for this belief.
At the time Kishkinda itself was undergoing a turmoil of a power struggle between the monkey princes Vali and Sugreeva. The more formidable Vali chases Sugreeva out of the kingdom. He takes refuge at Matunga Hill, which Vali can not access thanks to a curse on him.
Hanuman, the leader of the Sugreeva’s soldiers mistakes Rama and Lakshmana for Vali’s men. He quizzes them in disguise. On realizing it was Rama, Hanuman becomes his staunch follower of Rama.
A deal finally evolves between Rama and Sugreeva. Rama kills Vali and installs Sugreeva as the king of the monkey kingdom. Hanuman prepares to fly to Lanka in search of Sita.
As a tourist to Hampi, you can visit the places that are associated with this episode in Ramayana.
The whole of Hampi’s landscape is attributed as the mythical kingdom of monkeys. The Anjaneya Hill , just across the river is believed to be the place where Añjana gave birth to Hanuman.
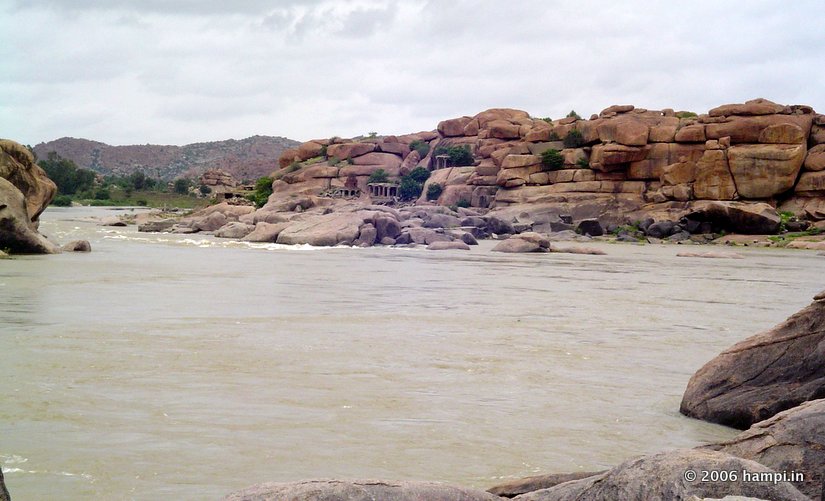
Rishimukh island is the place where Hanuman first meets Rama and Lakshmana. This is a holy place for the Hindus. You can spot a hermitage at the center of this island . A bit east in the island is the Chandramouleshwara Temple .
Sugreeva’s Cave is located on the banks of the river on the way to Vittala Temple. While Ravana taken Sita by the flying chariot , Sita dropped her jewels as a sign to aid Rama. Sugreeva find the fallen jewels and safe keeps in the caves. Later he shows it to Rama and asserts that it was Ravana who has abducted Sita. Even the marks on the rock surface here are equated with the motifs on Sita’s sari (costume). Next to it is a pond known after Sita’s name.
There is a temple called Chintamani at the Anegondi area on the edges of the river. This cave is where, according to local beliefs, Rama met Sugriva along with Hanuman. At Chintamani is a footprint impression on the rocky sheet. It's considered as the spot from where Rama aimed at Vali and shot the arrow.
Chintamani is the name of a precious stone (jewel), Rama gave Hanuman to identify him as Rama's messenger. It's believed that it's at this location Rama gave this jewel to Hanuman, as Sita can easily identify it.
The riverbank near Kodandarama Temple , near the Sugreeva’s cave is the place where Rama crowned Sugriva after killing Vali.
Malyavanta Hill , located almost at the south fringes of the ruins site has a temple dedicated to Rama at its summit. Rama and Lakshmana waited here during the rainy season before raiding Lanka. A cleft on top of the hill is believed to have caused by Lakshmana’s arrow.
Chapter Five - Sundara Kanda - deals with the flight of Hanuman to Lanka and his adventures there. Hanuman meets Sita and brings the new to Rama.
Chapter Six -Yuddha Kanda - narrates the Lanka war and the Rama-Ravana battle. Triumphant Rama returns to Ayodhya with Sita. The chapter ends with Rama’s coronation as the new king of Ayodhya.
The Seventh and the last chapter - Uttara Kanda - deals with life of Rama and Sita after their return. Also the chapter narrates Sita's banishment pass on to the next world.

Hamuman in Lanka
Hamuman in Lanka

Lord Rama . Image from Pattabhirama Temple
Lord Rama . Image from Pattabhirama Temple
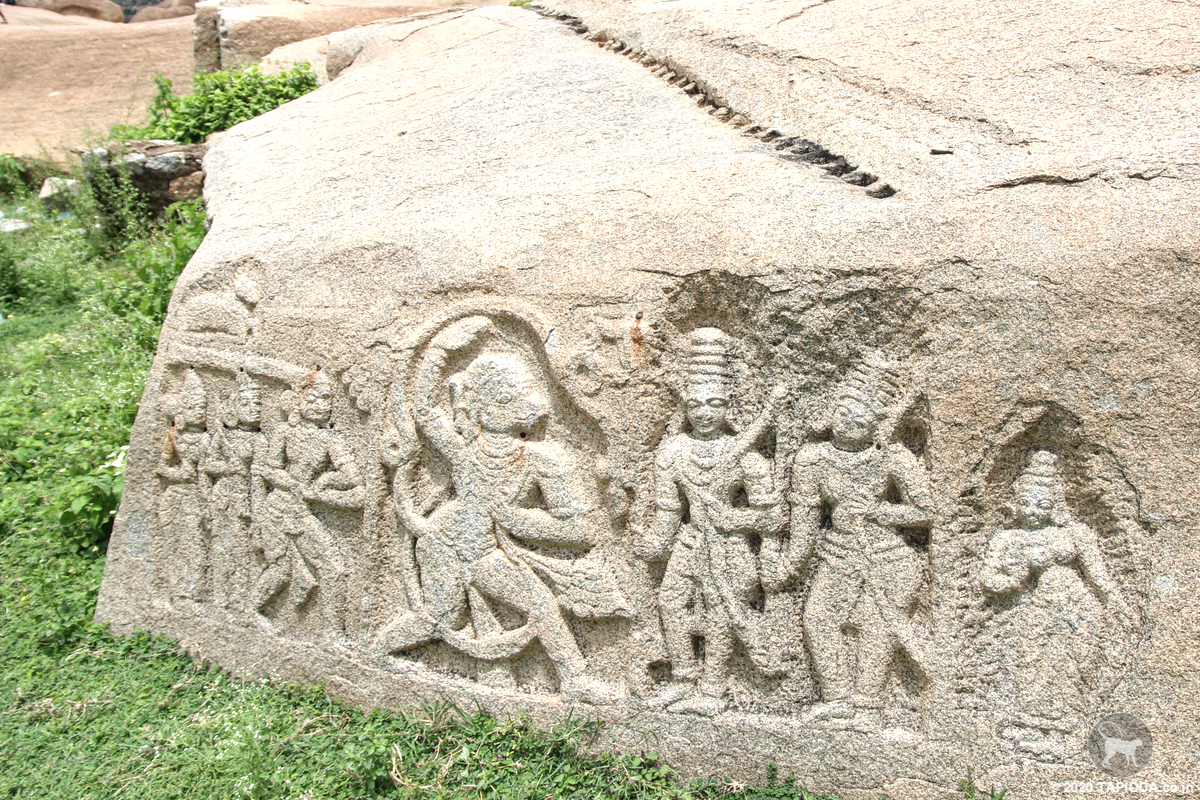

carving at Hemakuta hill
Hanuman Meets Rama and Lakshmana who was in search of the abducted Sita, Rama's wife.
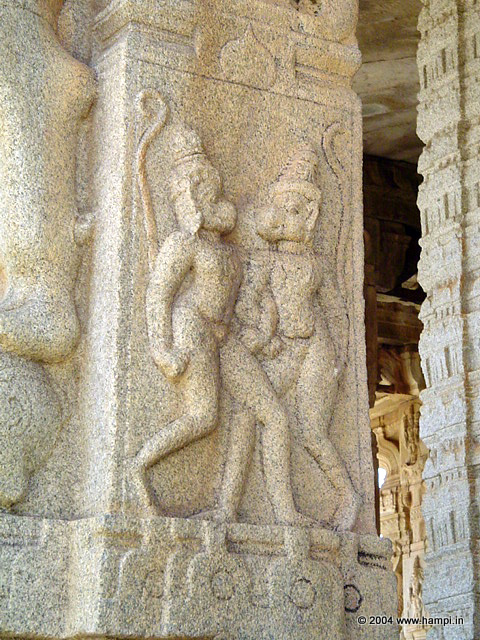
Vali and Sugreeva fighting
Vali and Sugreeva fighting. Image on the pillars of Vittala Temple
